
You're on your way!
You're being directed to a third-party site to get a quote.
Since 2011, we've helped more than 5 million visitors understand Medicare coverage.
By shopping with third-party insurance agencies, you may be contacted by a licensed insurance agent from an independent agency that is not connected with or endorsed by the federal Medicare program.
These agents/agencies may not offer every plan available in your area. Please contact Medicare.gov or 1-800-Medicare to get information on all options available.
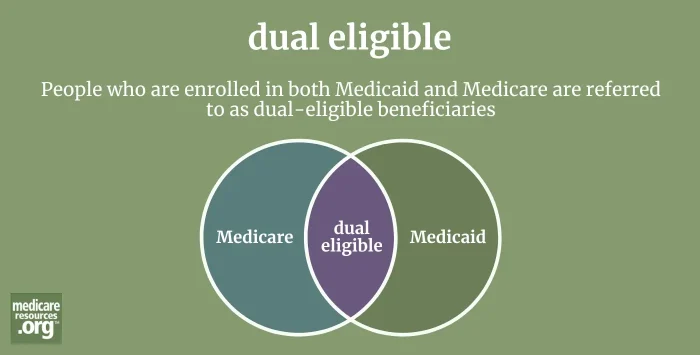
Americans who are enrolled in both Medicaid and Medicare are referred to as dual-eligible beneficiaries, or Medicare dual eligibles, or sometimes just duals.
Dual-eligibles are enrolled in both programs when a Medicare enrollee’s income and assets are low enough to qualify them for Medicaid help in paying for some of the costs of Medicare – or to qualify them for full coverage under both Medicare and Medicaid. (Note that for people who are disabled or at least 65 years old, Medicaid has both income and asset limits, as opposed to the income-based eligibility rules that apply to non-disabled people under age 65.)1
Dual-eligibles include two categories of beneficiaries:
Full-benefit dual-eligibles can enroll in Dual-Special Needs Plans (D-SNPs), which are the largest category of SNPs (the others are I-SNPs for Medicare beneficiaries who are institutionalized, and C-SNPs for beneficiaries with certain chronic medical conditions, but those account for only a small fraction of all SNP enrollments; most are D-SNPs).2
There are nearly 13 million dual-eligibles in the United States.3Most of them are eligible for full Medicaid benefits.4
Read more about dual eligibles.
Footnotes